Introduction
The Calcium Score Test for heart health, also known as a coronary artery calcium (CAC) test, is an advanced diagnostic tool that plays a vital role in assessing your risk of heart disease. With heart disease being the leading cause of death globally, this test helps detect early signs of atherosclerosis by measuring the amount of calcium in the coronary arteries. Understanding your calcium score can provide critical insights into your cardiovascular health.
1. What Is a Calcium Score Test?
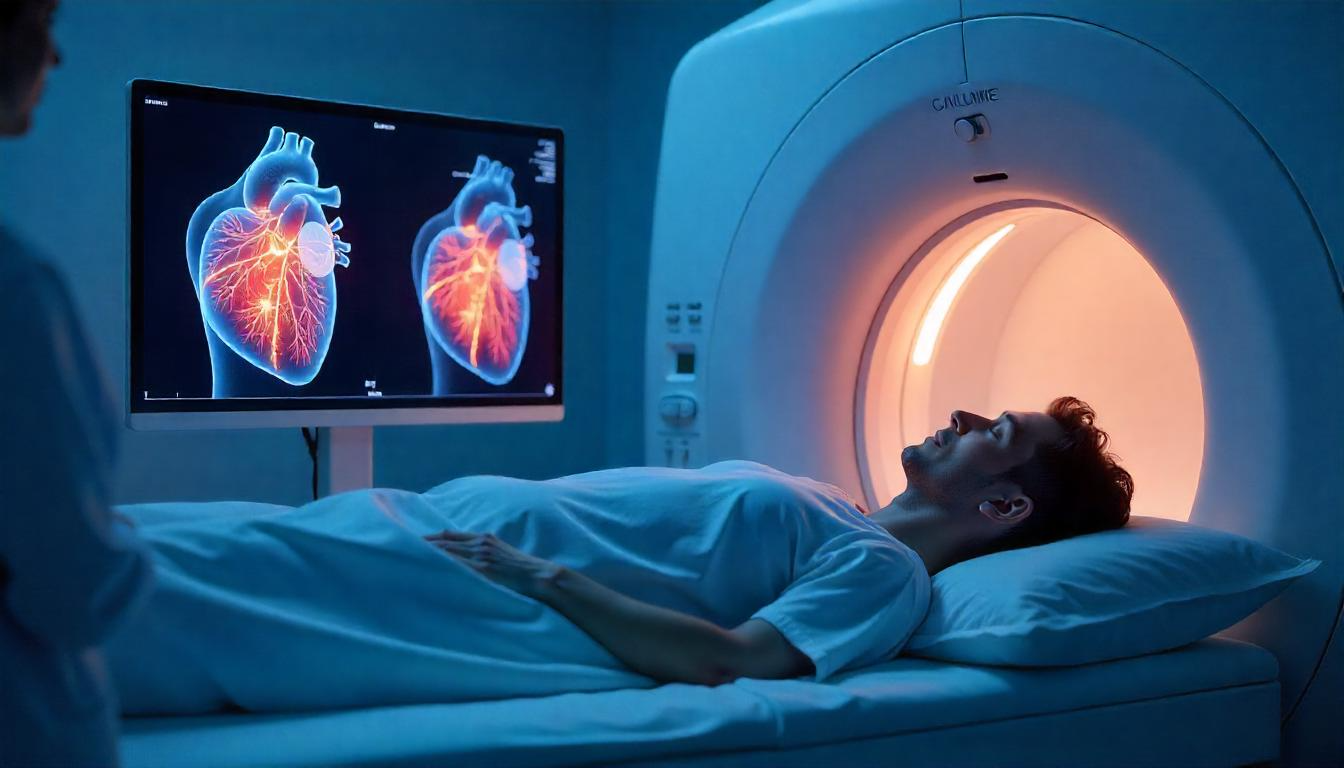
The Calcium Score Test is a non-invasive CT scan of the heart that checks for calcium buildup in the coronary arteries. This calcium is a sign of plaque, which can narrow or block the arteries and potentially lead to heart attacks.
How It Works
- The test uses a specialized X-ray (CT scanner) to capture detailed images of your heart.
- It quantifies the amount of calcium in your arteries, giving you a calcium score.
- The score helps doctors determine your risk for coronary artery disease (CAD).
2. How the Calcium Score Test Works
The test uses a specialized X-ray (CT scanner) to capture detailed images of your heart. It measures the total amount of calcium in your coronary arteries and assigns you a “calcium score.”
What the Score Means
- 0: No calcium, very low heart disease risk.
- 1–99: Mild calcium, low risk.
- 100–399: Moderate plaque buildup, moderate risk.
- 400+: Significant plaque, high risk of heart disease.
3. Why the Calcium Score Test Matters for Heart Health
Coronary artery disease often develops silently over the years. The Calcium Score Test for heart health can catch it before symptoms appear. The Calcium Score Test can catch it before symptoms appear.
Key Benefits:
- Detects heart disease early
- Assists in determining the need for lifestyle changes or medications
- Helps avoid unnecessary invasive procedures
Risk Levels Based on Scores:
- 0: No plaque – Low risk
- 1–99: Small amount – Mild risk
- 100–399: Moderate plaque – Moderate risk
- 400+: Extensive plaque – High risk of heart disease
4. Who Should Get a Calcium Score Test?
Those with an intermediate risk of heart disease benefit most from this test.
You may be a good candidate if you:
- Are between 40–70 years old
- Have a family history of heart disease
- Smoke or used to smoke
- Have high blood pressure, cholesterol, or diabetes
- Live a sedentary lifestyle
If you’re experiencing chest pain or other symptoms, your doctor may recommend additional tests.
How to Prepare for the Test
Preparation for a Calcium Score Test is minimal:
- No caffeine or smoking 4 hours before
- Avoid wearing metal objects
- No need to fast
The test typically takes 10–15 minutes and involves no injections or dyes.
5. Risks and Limitations of the Calcium Score Test
While the calcium score test is generally safe, it’s important to understand its potential drawbacks. The test does not detect soft plaque, and it may not be necessary for everyone. Knowing these limitations helps in making an informed decision with your healthcare provider.
How It Works
The scan uses low-dose CT imaging to measure calcium deposits in the arteries. While radiation exposure is minimal, it still exists, making the test unsuitable for frequent repetition.
Limitations
- Does not detect all types of plaque.
- May lead to unnecessary follow-up tests.
- Not recommended for very low-risk or high-risk individuals, where other tests may be more appropriate.
6. Cost and Insurance Coverage for the Calcium Score Test
The cost of a calcium score test can vary depending on your location and healthcare provider. In many cases, insurance may not cover the expense unless it’s deemed medically necessary. Understanding costs beforehand can help you prepare.
How It Works
Most hospitals and diagnostic centers offer the test at a fixed rate, which can range from affordable screening fees to higher costs in specialized facilities.
Benefits
- Transparent pricing allows you to plan ahead.
- Some community health events may offer the test at discounted rates or free of charge.
7. Who Should and Shouldn’t Get the Calcium Score Test
This test is most beneficial for people at intermediate risk of heart disease. However, it’s not suitable for everyone, such as those with known coronary artery disease or very low risk. Discussing your personal risk factors with a doctor ensures the best choice.
How It Works
A risk assessment, often including cholesterol tests and blood pressure checks, is done before recommending the calcium score test.
Benefits
- Helps target preventive care to the right patients.
- Avoids unnecessary testing for those unlikely to benefit.
What the Results Mean
Your calcium score provides a numeric value that reflects your heart’s health:
| Calcium Score | Risk Level | Suggested Action |
| 0 | Low | Continue a healthy lifestyle |
| 1–99 | Mild | Discuss lifestyle improvements with the doctor |
| 100–399 | Moderate | Medication and lifestyle changes |
| 400+ | High | Aggressive treatment, additional testing |
Your doctor will combine your calcium score with other factors like cholesterol and blood pressure to guide treatment.
Lifestyle Tips to Support Heart Health
Whether your calcium score is low or high, healthy habits can make a big difference:
- Eat Calcium-Rich Foods – Check out this guide to calcium-rich foods.
- Exercise Regularly – Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
- Quit Smoking – Smoking damages blood vessels and speeds up plaque buildup.
- Monitor Your Calcium Intake – Learn the difference between calcium citrate and calcium carbonate.
- Balance Your Nutrients – Include foods with calcium and vitamin D.
- Know Your Numbers – Understand normal calcium levels in blood.
- Address Deficiencies – Learn about calcium deficiency in women.
Recommended Supplement
If your doctor suggests calcium supplementation, this Calcium Citrate with Vitamin D3 supplement on Amazon is a top-rated, well-absorbed option.
Trusted External Resource
For more insights, check out the American Heart Association’s guide to heart scans.
FAQs About Calcium Score Test
Q1. Is the Calcium Score Test painful?
No, it simply takes a few minutes and is a quick and painless CT scan.
Q2. Does insurance cover this test?
It depends on your provider. Some may require a doctor’s referral.
Q3. What if I get a high score?
Plaque accumulation is indicated by a high score. Your physician might suggest medication, lifestyle modifications, or additional tests.
Q4. How often should I get tested?
You might not need to take the test again for five years if you received a low or zero score. If your score is high, follow your doctor’s advice closely.
Q5. Can I reduce my calcium score?
You can’t reduce existing plaque, but you can prevent further buildup with healthy lifestyle changes and treatment.
Conclusion: Take Charge of Your Heart Health Today
The Calcium Score Test for heart health is a powerful preventive tool that provides vital information about your heart’s condition. If you fall into the moderate-risk category, talk to your healthcare provider to determine whether this test is right for you. Early detection can save lives.
Call to Action
Take control of your heart health today. Schedule a Calcium Score Test with your doctor and explore resources to improve your cardiovascular wellness. Don’t forget to share this article with friends and family who might benefit!
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and is not intended to replace professional medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment options specific to your condition.

Recent Comments